In the battle against wildlife poaching and habitat destruction, innovative technologies are playing a crucial role in safeguarding endangered species and preserving biodiversity. One such cutting-edge advancement is the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in wildlife conservation. Camera traps equipped with AI capabilities are revolutionizing the way conservationists monitor wildlife and combat poaching efforts.
Poaching refers to the illegal hunting, capturing, or killing of wildlife. This practice poses a severe threat to numerous species around the world, driving many to the brink of extinction. Poaching often targets high-value animals for their body parts, such as rhinos for their horns, elephants for their tusks, and tigers for their pelts.
The ramifications of poaching extend beyond individual species. When populations of animals decline rapidly, it disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems. The removal of key species can lead to a cascade of effects, ultimately endangering many other organisms that depend on these species for survival. Moreover, poaching contributes to habitat degradation, loss of biodiversity, and the weakening of ecological resilience.
In many regions, poaching is driven by poverty and lack of alternative livelihoods. However, the long-term consequences of wildlife loss can have profound economic implications for communities that rely on tourism and healthy ecosystems. Additionally, poaching often fuels corruption, organized crime, and violence, undermining governance and social stability.

Historically, wildlife monitoring has primarily relied on human observers, ranger patrols, and static camera traps. While these methods have proven beneficial, they come with significant limitations. Ranger patrols can be resource-intensive and may not cover vast or remote areas. Traditional camera traps, though useful for capturing images, require manual checks, which can jeopardize the detection of poaching incidents.
The advent of technology has ushered in new possibilities in wildlife monitoring. Emerging solutions, including drones, satellite imagery, and AI, are enhancing conservation efforts, allowing for more efficient and reliable systems of tracking wildlife and detecting poaching activities.
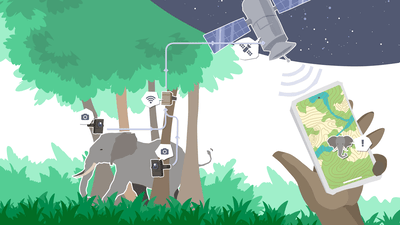
AI-powered camera traps combine the capabilities of advanced machine learning algorithms with the traditional function of wildlife cameras. These intelligent systems can automatically analyze images captured in the field, identifying animals and even distinguishing between human activity and wildlife interactions. This breakthrough allows for quicker responses to poaching threats and more effective wildlife management.
AI camera traps are equipped with motion-activated cameras that capture images or videos when they detect movement. These traps are strategically placed in areas frequented by wildlife, including migration paths and known poaching hotspots.
Once images are captured, they are transmitted to a central database using wireless connectivity. This allows conservationists to access the data remotely, ensuring timely monitoring and analysis.
The core feature of AI camera traps lies in their ability to analyze images using machine learning algorithms. These algorithms are trained on vast datasets of images to recognize different species and differentiate between animals and humans. This reduces the need for manual review of thousands of photos, saving time and effort for conservation teams.
When the AI identifies potential poaching activity, it can trigger real-time alerts to field staff or rangers. This rapid response capability is crucial for addressing threats before they escalate.
AI models continuously improve their accuracy through machine learning. By analyzing new data and feedback from users, the system becomes more adept at recognizing wildlife patterns and detecting poachers over time.

AI camera traps significantly reduce the labor required for wildlife monitoring. By automating image analysis, conservationists can focus their efforts on critical decision-making and intervention strategies rather than sifting through countless images.
The ability of AI camera traps to detect poaching activity in real time drastically improves response times. Rapid alerts empower rangers to act swiftly, increasing the likelihood of apprehending poachers and deterring future incidents.
AI algorithms can accurately identify a wide range of species, even in challenging conditions or low-light environments. This capability enhances data collection on various wildlife populations, informing conservation efforts and species management strategies.
Many areas prone to poaching are remote and difficult to access. AI camera traps can be deployed in these locations, providing continuous monitoring without the need for constant human presence, thereby minimizing disturbance to wildlife.
While the initial investment in AI technology may be significant, the long-term savings associated with reduced labor costs and more efficient monitoring systems can make AI camera traps a cost-effective solution for conservation agencies.
The African Parks Network, a conservation organization that manages protected areas across Africa, has implemented AI camera traps in several of their sites. In one notable case, the integration of AI technology led to a 60% reduction in poaching incidents within a year. Real-time alerts enabled rangers to intervene during active poaching attempts, showcasing the power of technology in wildlife protection.
In Tanzania's Ruaha National Park, the Wildlife Conservation Society introduced AI camera traps to monitor elephant populations and deter poaching. The results were remarkable – not only did the technology provide valuable data on elephant movements, but it also helped increase ranger efficiency and reduce human-wildlife conflicts in surrounding communities.
The Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute has partnered with tech companies to deploy AI camera traps in various ecosystems. Their research focused on identifying rare and endangered species, such as the elusive snow leopard. The technology has enabled more accurate population estimates and helped target conservation efforts effectively.
In Madagascar, where unique species face dire threats, Conservation International has utilized AI camera traps to monitor the critically endangered lemur population. The system has helped identify poaching hotspots, allowing for targeted law enforcement efforts. Additionally, the project has engaged local communities in conservation and awareness initiatives, promoting a collaborative approach to wildlife protection.

While AI-powered camera traps represent a significant advancement in wildlife conservation, there are challenges and considerations to keep in mind.
The use of camera traps raises concerns about data privacy, especially when human activities are monitored. Ensuring that image data is handled responsibly and securely is essential to maintaining community trust and compliance with legal frameworks.
The effectiveness of AI camera traps relies on the quality and training of the algorithms used. Accurate training requires diverse and comprehensive datasets. Insufficient data can lead to misidentification or failures in recognizing poaching activity, potentially undermining conservation efforts.
While AI camera traps can save costs in the long run, the initial investment can be substantial, particularly for initiatives in developing regions. Conservation organizations must secure funding and resources to implement these technologies sustainably.
For AI camera traps to be most effective, local teams must be trained not only in operating the technology but also in interpreting data and responding to alerts. Capacity building is crucial for empowering communities and ensuring successful conservation outcomes.
AI camera traps should complement traditional conservation methods, not replace them. Combining AI technology with ranger patrols, community engagement, and habitat management creates a holistic approach to combating poaching and promoting biodiversity.
The future of wildlife conservation is bright, with AI technology at the forefront of innovative solutions. Several trends are likely to shape the evolution of AI applications in this field:
As AI technology advances, machine learning algorithms will become more sophisticated, allowing for improved accuracy in detecting poaching and recognizing species. Algorithms will also adapt to new conditions and scenarios, making them increasingly robust in various ecological contexts.
The integration of AI camera traps with other technologies, such as drones and satellite imagery, can create a comprehensive monitoring system. This convergence will enhance situational awareness and provide a multi-faceted approach to wildlife protection.
Collaboration among governments, NGOs, tech companies, and local communities will become increasingly important. Partnerships can facilitate knowledge sharing, technological transfer, and funding opportunities, leading to more effective conservation strategies.
Engaging local communities in wildlife conservation efforts will be crucial for the sustainability of projects. By involving communities in the monitoring and protection of wildlife, conservationists can foster a sense of ownership and stewardship, ensuring long-term success.
As AI-driven innovations become more widespread, robust policies and regulations will be needed to govern their use. Advocacy for stronger wildlife protection laws and enhanced enforcement measures will be vital in safeguarding biodiversity effectively.
AI-powered camera traps represent a transformative advancement in wildlife conservation, offering efficient and effective tools for combating poaching and monitoring wildlife populations. By harnessing the capabilities of artificial intelligence, conservationists can improve their responses to threats, better understand ecosystems, and foster collaboration with local communities.
As challenges related to poaching and habitat loss continue to escalate, the integration of technology in conservation efforts becomes increasingly essential. Through innovative approaches like AI camera traps, we have the potential to create a sustainable future for wildlife, ensuring that future generations can experience the rich biodiversity of our planet.